The choice between circular polarization antennas and linear polarization antennas can make a significant difference in an RFID system.
Linear polarization occurs when electromagnetic waves broadcast on a single plane (either vertical or horizontal). Linear polarized antennas must have a known RFID tag orientation and the RFID tag must be fixed upon the same plane as the antenna in order to get a consistent read. Some examples of linear polarized antennas are the MTI MT-263003 Outdoor Antenna, and the Times-7 A5531 Indoor Antenna.
Due to the concentrated emission, linear polarized antennas typically have greater read range than circular polarized antennas of the same gain.
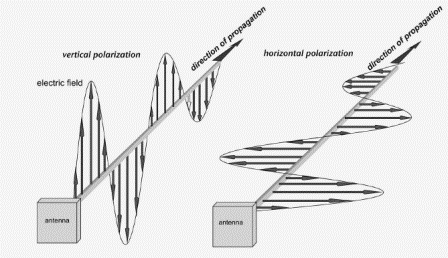
Linear Polarized Antenna
Circular polarized antennas, such as the Laird S9028PCR Indoor RFID Antenna and the MTI MT-242043 Outdoor RFID Antenna, emit electromagnetic fields in a corkscrew-like fashion. Technically speaking, they are broadcasting electromagnetic waves on two planes making one complete revolution in a single wavelength.
Compared to linear polarized antennas of the same gain, circular polarized antennas will have a shorter read range because they lose about 3 dB splitting their power across two separate planes.
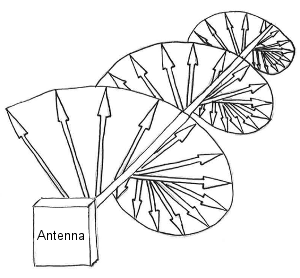
Circular Polarized Antenna
When deciding which type of antenna to purchase for your RFID system, understanding the how these antennas work as well as how the RFID tags should be oriented with respect to the antennas is key.
If all the tags you need to read will be on the same plane and aligned with the plane of the antenna, then you should consider a linear polarized antenna. If your tag orientation is not something that will be reliable or consistent, then you will likely need to use a circular polarized antenna.
Conclusion
If you would like to learn more about all things RFID, check out our website, or contact us.